What are CAE’s?
These are Energy Savings Certificates that validate the
energy consumption reductions achieved through
of the implementation of energy efficiency measures.
What are CAE’s?
They are Energy Saving Certificates that validate the reduction of energy consumption reduction of energy consumption achieved through the implementation of the implementation of energy efficiency measures.

History of CAE
Why do CAEs exist?
In the European Union and Spain, companies have a responsibility to contribute to energy efficiency and the reduction of carbon emissions. This is governed by European and national regulations.
The National System of Energy Efficiency Obligations (SNOEE) establishes energy-related companies as Obligated Parties (SO). These SOs have an energy efficiency obligation, and if they do not generate it, they must pay a savings quota.
This can be settled through financial contributions to the National Energy Efficiency Fund and by using Energy Saving Certificates (CAE). The Institute for Energy Diversification and Saving (IDAE) invests these resources in projects that promote energy saving and energy efficiency in different national sectors.

Definition of CAE
So, what are CAE’s?
Also known as white certificates, an Energy Saving Certificate (ESC) is a document that guarantees that, after carrying out an energy efficiency action, a new final energy saving equivalent to 1 kWh has been achieved. Thus, if an action is undertaken that implies a new annual saving of 1000 kWh (equivalent to 1 MWh), 1000 EECs can be obtained.
1 CAE = 1 kWh of final energy savings
* 1000 CAE = 1000 kWh = 1 MWh of energy savings



Working with Polestar Energy
How does the sale and purchase work?
In Spain, there is a secondary market that allows companies that have not met their energy efficiency targets to purchase CAE to meet their commitments to the National Energy Efficiency Fund (FNEE), while those that have exceeded their targets can sell surplus certificates. This allows:
- Monetize energy savings.
- Promote investment in energy efficiency.
We at Polestar Energy are intermediaries in the sale and purchase of CAEs.

Are you an energy efficiency producer or an energy distributor?
Producer
With Polestar Energy monetize your energy savings and receive additional income.
Distributor
With Polestar Energy, you turn energy efficiency into a profitable investment.

Benefits of the CAE system
Monetize the energy savings obtained by the energy efficiency producer.
2. Increase the market for energy efficiency products, services and technology.
3. Achieve energy savings at lower cost, increasing profitability.
4. To make compliance with part of the obligations of the regulated entities more flexible.
5. Promote investment in energy efficiency.
6. Generate non-energy benefits by boosting employment, productivity and competitiveness.
Benefits of the CAE system
Monetize the energy savings obtained by the energy efficiency producer.
2. Increase the market for energy efficiency products, services and technology.
3. Achieve energy savings at lower cost, increasing profitability.
4. To make compliance with part of the obligations of the regulated entities more flexible.
5. Promote investment in energy efficiency.
6. Generate non-energy benefits by boosting employment, productivity and competitiveness.

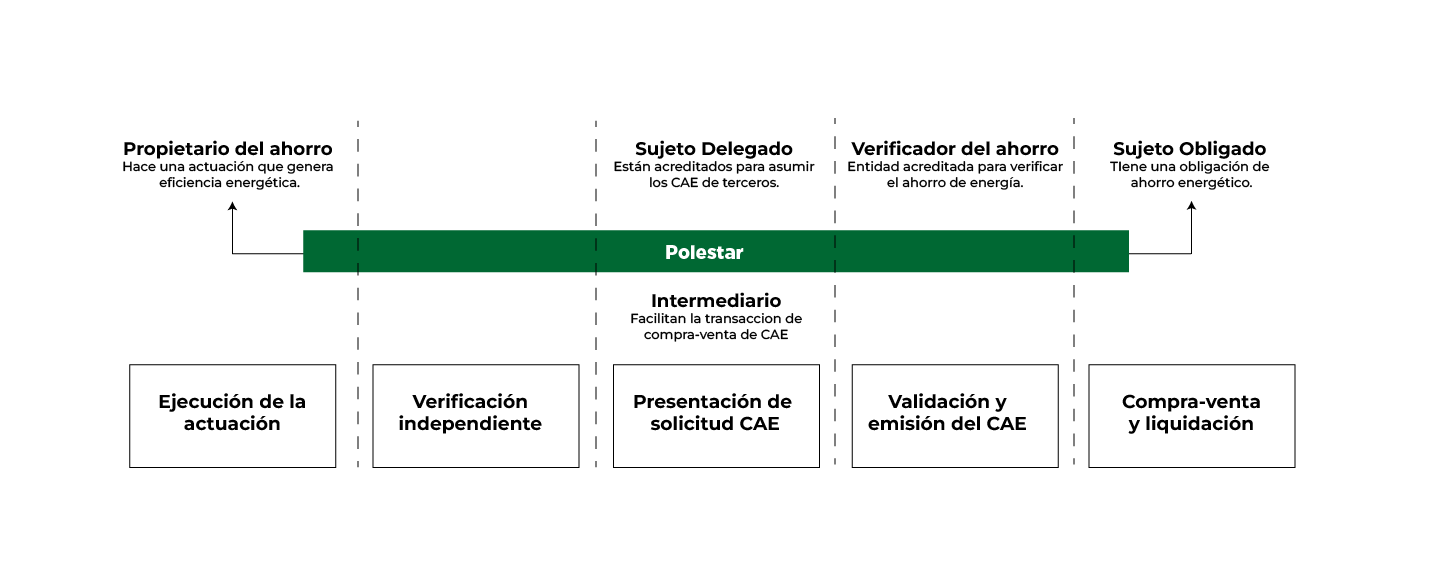
Who are the important important players?
End user or beneficiary
That natural or legal person who, being the owner, lessee or occupant of the installations on which the energy efficiency action has been carried out, obtains a positive impact from the final energy savings generated.
Generally speaking, it is also the person who decides to carry out such improvement action and who executes the initial investment for it. Most likely, the beneficiary will also have the title of Final Energy Saving Owner, unless he/she has signed an assignment agreement with a third party.
Owner of final energy savings
Natural or legal person of a public or private nature that carries out the investment of the energy efficiency performance with the purpose of obtaining final energy savings, for itself or for a third party. It can also be the one to whom the savings generated by such action have been assigned.
As an example, a municipality decides to carry out a certain action and as a consequence of this decision signs an energy performance contract with a company. In this case, the original owner of the savings will be the municipality, not the company.
In the event that the municipality has signed an assignment agreement with the company, the company would be the owner of the savings.
Delegated Subject
Legal entity of a public or private nature that can assume, totally or partially, the delegation of obtaining new annual energy savings from one or more obligated parties.
Energy Savings Verifier
Entity accredited by the National Accreditation Entity (ENAC) in charge of verifying the energy savings obtained by the implementation of one or more energy efficiency actions.
It may be freely chosen by the obligor or the delegated party from among those that provide this service.
Obligor
Gas and electricity trading companies, wholesale petroleum product operators and wholesale liquefied petroleum gas operators.
They have an obligation to save energy after 2 years of operation and must compensate emissions through an annual contribution to the SNOEE through a contribution to the FNEE and a part can be compensated through the CAE.
Who are the important important players?
End user or beneficiary
That natural or legal person who, being the owner, lessee or occupant of the installations on which the energy efficiency action has been carried out, obtains a positive impact from the final energy savings generated.
Generally speaking, it is also the person who decides to carry out such improvement action and who executes the initial investment for it. Most likely, the beneficiary will also have the title of Final Energy Saving Owner, unless he/she has signed an assignment agreement with a third party.
Owner of final energy savings
Natural or legal person of a public or private nature that carries out the investment of the energy efficiency performance with the purpose of obtaining final energy savings, for itself or for a third party. It can also be the one to whom the savings generated by such action have been assigned.
As an example, a municipality decides to carry out a certain action and as a consequence of this decision signs an energy performance contract with a company. In this case, the original owner of the savings will be the municipality, not the company.
In the event that the municipality has signed an assignment agreement with the company, the company would be the owner of the savings.
Delegated Subject
Legal entity of a public or private nature that can assume, totally or partially, the delegation of obtaining new annual energy savings from one or more obligated parties.
Energy Savings Verifier
Entity accredited by the National Accreditation Entity (ENAC) in charge of verifying the energy savings obtained by the implementation of one or more energy efficiency actions.
It may be freely chosen by the obligor or the delegated party from among those that provide this service.
Obligor
Gas and electricity trading companies, wholesale petroleum product operators and wholesale liquefied petroleum gas operators.
They have an obligation to save energy after 2 years of operation and must compensate emissions through an annual contribution to the SNOEE through a contribution to the FNEE and a part can be compensated through the CAE.
Frequently Asked Questions from CAE
What is energy efficiency?
Energy efficiency is the ability to obtain the best results in any activity using the least amount of energy possible.
The Energy Saving Certificates (CAEs) were created as a mechanism to promote energy efficiency. The system was initiated with Royal Decree 36/2023 of January 26, 2023.
What is SNOEE and FNEE?
The European Regulation and its Spanish transposition obliges Obligated Parties (SO) to to commit to saving energy from their annual sales. This obligation has resulted in a financial contribution by these SOs to the National Energy Efficiency Fund (FNEE).
This FNEE is used by the State as a mechanism to channel financial resources towards initiatives that help optimize energy use, in order to improve environmental sustainability and strengthen the country’s energy security.
What are Energy Saving Certificates (ESC)?
A Certificate of Energy Saving (CAE) is a document that guarantees that, after carrying out an energy efficiency action, a new final energy saving equivalent to 1 kWh has been achieved. Thus, if an action is undertaken that implies a new annual saving of 1000 kWh (equivalent to 1 MWh), 1000 CAE can be obtained.
This instrument makes it possible to monetize energy savings, recovering part of the cost of investments in energy efficiency (change of lighting, improvement of thermal insulation, renovation of industrial or domestic equipment, etc.), since the end user will be able to receive a consideration if he sells the savings obtained for subsequent certification through the CAE System.
What are the CAE's for?
Annually, a final energy savings obligation is imposed on obligated entities (SO). The presentation of CAE is an alternative and voluntary instrument to the economic contribution to the National Energy Efficiency Fund for the compliance of such obligation.
What actions give rise to CAE?
To obtain CAE, companies or entities must implement energy efficiency measures in their facilities or processes.
Theoretically, it applies to any action that results in energy savings. These measures can range from installing more efficient equipment to optimizing industrial processes to reduce energy consumption.
In practice, there will be two types of actions:
- Standardized: They are included in a catalog, have characteristics and technical particularities and are justifiable through cards already predefined by the BOE.
- Singular: They are out of the catalog. Requires specific intervention by an official savings verifier to apply for CAE.
Photovoltaic is not included, as it does not involve final energy savings (solar thermal, however, can generate CAE as long as it is not a mandatory action).
Once the measures have been implemented, the energy savings obtained are calculated and the corresponding certificates are issued.
What is the value of a CAE?
A CAE has a single value of 1kWh of final energy consumption savings.
1 CAE = 1KWh of final energy savings.
1000 CAE = 1Mwh of final energy savings.
As for the monetary value, the National Coordinator of the PPA System will provide, from the electronic platform, the average price of the sale of PPAs.
How are the savings that can generate CAE calculated?
Within the CAE System, both in standardized actions and in singular actions, only the final energy savings achieved in one year will be taken into account, not the accumulated savings throughout the useful life of the action.
Obligated parties are assigned a nationwide annual energy savings quota, known as savings obligations. This savings obligation is expressed in GWh/year or its equivalent in kWh/year.
What is the deadline to register the CAE?
A CAE may be registered up to three years after the performance that generated the certified energy savings has been carried out, provided that the execution of the performance has started since the date of entry into force of the Royal Decree (January 26, 2023) and before January 1, 2031.
How long is a CAE valid?
The CAE will be valid for three (3) years from the date on which the performance of the action generating the energy savings was completed (when the savings begin to be generated), or until December 31, 2030 (inclusive), whichever is earlier.
Once a CAE reaches its expiration date it will lose its validity.
Who can be a CAE holder?
Holder of the CAE: It can only be an obligated subject (SO) or a delegated subject (SD) in favor of whom a CAE has been issued or who has acquired it through a legal purchase and sale business.
If I make an action that generates energy savings, can I sell those savings? Can I sell the energy savings generated by my actions?
In this case, you will be considered an Energy Saving Owner, in accordance with the provisions of Article 12.1 of Royal Decree 36/2023, of January 24, which establishes a system of Energy Saving Certificates.
Such energy savings may be transferred to a third party by signing a private agreement or directly to an SO or SD by signing a CAE Agreement (Royal Decree 36/2023, January 24, Article 12.1; Order TED/815/2023, July 18, Article 11).
What is a CAE Agreement?
The CAE agreement is an agreement signed between the obligated entity or the delegated entity and the owner of the energy savings, whereby the latter assigns such savings to the obligated entity or the delegated entity in exchange for a consideration.
What is a delegation contract?
The delegation contract is a private law agreement signed between an obligated subject and a delegated subject whereby the latter (SD) undertakes to obtain and settle on behalf of the former (SO) a number of CAE equivalent to a given amount of final energy savings.
It is recalled that in no case the delegated subject assumes the annual obligation, in whole or in part, of the obligated subject or the condition of obligated subject, maintaining in any case the referred obligation in the obligated subject.
Who issues the CAE?
The body or entity responsible for energy efficiency in the autonomous community where the energy saving action has been carried out (autonomous community manager).
For this purpose, the obligor or the delegated subject must submit a request to the regional manager for the issuance of the CAE, together with a file that includes the favorable opinion and the verifier’s report (Royal Decree 36/2023, January 24, Article 13).
Who is the National Coordinator of the CAE System?
The National Coordinator of the CAE System is the administrative body in charge of ensuring the correct operation of the CAE System. The national coordination of the PPA System will correspond to the General Directorate of Energy Policy and Mines of the Ministry for Ecological Transition and Demographic Challenge (Royal Decree 36/2023, January 24, Article 16).
What is the minimum amount of energy for which a CAE can be requested?
The minimum file size to make a request for the issuance of CAE is 30 MWh, which can be covered by the sum of the savings of the different actions (standardized and/or singular) included in the request (Order TED/815/2023, of July 18, Article 14.6).
Who can apply for CAE issuance?
Only those who have the consideration of obligated parties (SO) of the National System of Energy Efficiency Obligations (SNOEE) with an energy saving obligation equal to or greater than 50 MWh or who have been accredited as delegated parties (SD) can request the issuance of CAE (Order TED/815/2023, of July 18, Article 14.1).
You can find additional information on the CAE on the official website of the official website of the Ministry of Ecological Transition and the Demographic Challenge.
Frequently Asked Questions from CAE
What is energy efficiency?
Energy efficiency is the ability to obtain the best results in any activity using the least amount of energy possible.
The Energy Saving Certificates (CAEs) were created as a mechanism to promote energy efficiency. The system was initiated with Royal Decree 36/2023 of January 26, 2023.
What is SNOEE and FNEE?
The European Regulation and its Spanish transposition obliges Obligated Parties (SO) to to commit to saving energy from their annual sales. This obligation has resulted in a financial contribution by these SOs to the National Energy Efficiency Fund (FNEE).
This FNEE is used by the State as a mechanism to channel financial resources towards initiatives that help optimize energy use, in order to improve environmental sustainability and strengthen the country’s energy security.
What are Energy Saving Certificates (ESC)?
A Certificate of Energy Saving (CAE) is a document that guarantees that, after carrying out an energy efficiency action, a new final energy saving equivalent to 1 kWh has been achieved. Thus, if an action is undertaken that implies a new annual saving of 1000 kWh (equivalent to 1 MWh), 1000 CAE can be obtained.
This instrument makes it possible to monetize energy savings, recovering part of the cost of investments in energy efficiency (change of lighting, improvement of thermal insulation, renovation of industrial or domestic equipment, etc.), since the end user will be able to receive a consideration if he sells the savings obtained for subsequent certification through the CAE System.
What are the CAE's for?
Annually, a final energy savings obligation is imposed on obligated entities (SO). The presentation of CAE is an alternative and voluntary instrument to the economic contribution to the National Energy Efficiency Fund for the compliance of such obligation.
What actions give rise to CAE?
To obtain CAE, companies or entities must implement energy efficiency measures in their facilities or processes.
Theoretically, it applies to any action that results in energy savings. These measures can range from installing more efficient equipment to optimizing industrial processes to reduce energy consumption.
In practice, there will be two types of actions:
- Standardized: They are included in a catalog, have characteristics and technical particularities and are justifiable through cards already predefined by the BOE.
- Singular: They are out of the catalog. Requires specific intervention by an official savings verifier to apply for CAE.
Photovoltaic is not included, as it does not involve final energy savings (solar thermal, however, can generate CAE as long as it is not a mandatory action).
Once the measures have been implemented, the energy savings obtained are calculated and the corresponding certificates are issued.
What is the value of a CAE?
A CAE has a single value of 1kWh of final energy consumption savings.
1 CAE = 1KWh of final energy savings.
1000 CAE = 1Mwh of final energy savings.
As for the monetary value, the National Coordinator of the PPA System will provide, from the electronic platform, the average price of the sale of PPAs.
How are the savings that can generate CAE calculated?
Within the CAE System, both in standardized actions and in singular actions, only the final energy savings achieved in one year will be taken into account, not the accumulated savings throughout the useful life of the action.
Obligated parties are assigned a nationwide annual energy savings quota, known as savings obligations. This savings obligation is expressed in GWh/year or its equivalent in kWh/year.
What is the deadline to register the CAE?
A CAE may be registered up to three years after the performance that generated the certified energy savings has been carried out, provided that the execution of the performance has started since the date of entry into force of the Royal Decree (January 26, 2023) and before January 1, 2031.
How long is a CAE valid?
The CAE will be valid for three (3) years from the date on which the performance of the action generating the energy savings was completed (when the savings begin to be generated), or until December 31, 2030 (inclusive), whichever is earlier.
Once a CAE reaches its expiration date it will lose its validity.
Who can be a CAE holder?
Holder of the CAE: It can only be an obligated subject (SO) or a delegated subject (SD) in favor of whom a CAE has been issued or who has acquired it through a legal purchase and sale business.
If I make an action that generates energy savings, can I sell those savings? Can I sell the energy savings generated by my actions?
In this case, you will be considered an Energy Saving Owner, in accordance with the provisions of Article 12.1 of Royal Decree 36/2023, of January 24, which establishes a system of Energy Saving Certificates.
Such energy savings may be transferred to a third party by signing a private agreement or directly to an SO or SD by signing a CAE Agreement (Royal Decree 36/2023, January 24, Article 12.1; Order TED/815/2023, July 18, Article 11).
What is a CAE Agreement?
The CAE agreement is an agreement signed between the obligated entity or the delegated entity and the owner of the energy savings, whereby the latter assigns such savings to the obligated entity or the delegated entity in exchange for a consideration.
What is a delegation contract?
The delegation contract is a private law agreement signed between an obligated subject and a delegated subject whereby the latter (SD) undertakes to obtain and settle on behalf of the former (SO) a number of CAE equivalent to a given amount of final energy savings.
It is recalled that in no case the delegated subject assumes the annual obligation, in whole or in part, of the obligated subject or the condition of obligated subject, maintaining in any case the referred obligation in the obligated subject.
Who issues the CAE?
The body or entity responsible for energy efficiency in the autonomous community where the energy saving action has been carried out (autonomous community manager).
For this purpose, the obligor or the delegated subject must submit a request to the regional manager for the issuance of the CAE, together with a file that includes the favorable opinion and the verifier’s report (Royal Decree 36/2023, January 24, Article 13).
Who is the National Coordinator of the CAE System?
The National Coordinator of the CAE System is the administrative body in charge of ensuring the correct operation of the CAE System. The national coordination of the PPA System will correspond to the General Directorate of Energy Policy and Mines of the Ministry for Ecological Transition and Demographic Challenge (Royal Decree 36/2023, January 24, Article 16).
What is the minimum amount of energy for which a CAE can be requested?
The minimum file size to make a request for the issuance of CAE is 30 MWh, which can be covered by the sum of the savings of the different actions (standardized and/or singular) included in the request (Order TED/815/2023, of July 18, Article 14.6).
Who can apply for CAE issuance?
Only those who have the consideration of obligated parties (SO) of the National System of Energy Efficiency Obligations (SNOEE) with an energy saving obligation equal to or greater than 50 MWh or who have been accredited as delegated parties (SD) can request the issuance of CAE (Order TED/815/2023, of July 18, Article 14.1).
Additional information on the CAE can be found on the official website of the Ministry for Ecological Transition and the Demographic Challenge.
Process and participants
Process and participants

With PPAs, individuals and businesses work together towards a more sustainable future that promotes energy efficiency.
Case study
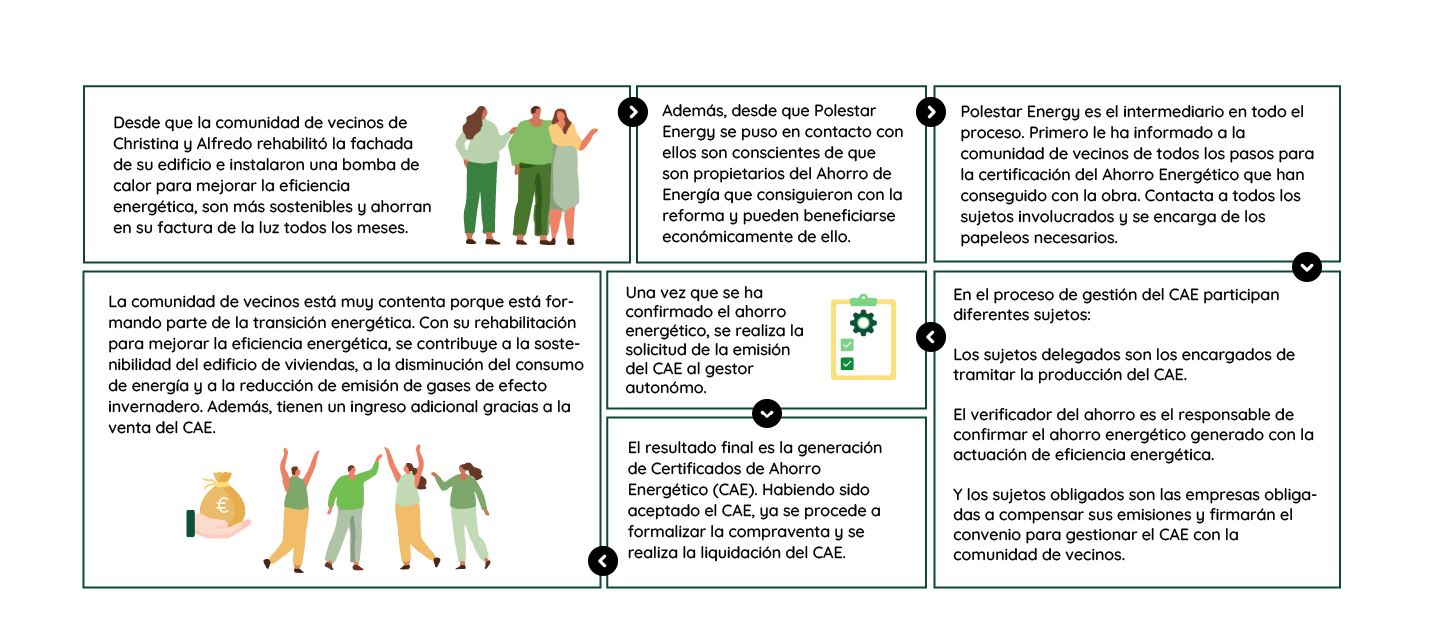
Case study

